AVANCE CASO
Mujer de 29 años
de edad, que comienza en el año 2014, 4 meses posteriores al parto de su primer
embarazo, comienza con una disnea de esfuerzo. Dichos síntomas fueron
progresando, por lo cual es internada 13 meses después del parto, donde se
efectuó el diagnostico de hipertensión pulmonar. Se encontraba asintomática
antes del embarazo, no tenía historia de abortos ni antecedentes personales, pero se realizo pruebas geneticas y se encontro antecedentes familiares de hipertensión pulmonar y trombo embolismo pulmonar por parte de abuelo materno. Curso un
parto normal, sin complicaciones, pero el parto resulto ser por medio de cesárea,
aunque el recién nacido no presento complicaciones.
CONTEXTUALIZACIÓN
La hipertensión pulmonar es una
enfermedad del corazón y pulmones ya que es alta tensión en las arterias pulmonares
pero esto hace que el corazón sobretodo la parte derecha, se esfuerce más en el
bombeo de sangre a los pulmones
Puede ser causada por: Artritis reumatoide,
anomalías en el corazón, embolia pulmonar, insuficiencia cardíaca, infección
por VIH, niveles bajos de o2, EPOC, fibrosis, apnea del sueño.
Sus síntomas más comunes son: Disnea,
mareo, sincope, presión o dolor en pecho, edema, pulso acelerado.
HISTORIA CLÍNICA
- Documento: CC. 010604060
- Lugar y fecha de nacimiento: Bogotá D.C 01/01/1991
- Estado civil: Soltera
- Dirección: Diagonal 3 #12 M
- Teléfono: 1974753
- Celular: 27548491
Anamnesis
- Edad: 29 años
- Genero: Femenino
- Hábitos de vida: No fuma, no bebe
- Consumo de fármacos: No
- Antecedentes familiares: hipertension pulmonar y tromboembolismo pulmonar por parte de abuelo materno
- Antecedentes personales: No presenta
- Imágenes diagnosticas: Ecocardiograma. electrocardiograma, radiografía de tórax, análisis de sangre, resonancia magnética.
- Actividad física: Cuando comenzaron los síntomas de disnea.
REVISIÓN POR SISTEMAS
En primera
instancia se realizó una evaluación por sistemas requerida por la guía APTA:
CARDIOVASCULAR
|
OSTEOMUSCULAR
|
MUSCULOESQULETICO
|
TEGUMENTARIO
|
Tensión arterial
|
Screening muscular
|
Marcha
|
Textura
|
Frecuencia cardiaca
|
Screening articular
|
Locomoción
|
Coloración
|
Tensión pulmonar
|
Peso
|
Balance
|
Temperatura
|
Frecuencia respiratoria
|
Talla
|
Traslaciones
|
Elasticidad
|
Temperatura
|
IMC
|
Consciencia
|
Integridad
|
Edema
|
Postura
|
Comportamiento
|
Pigmentación
|
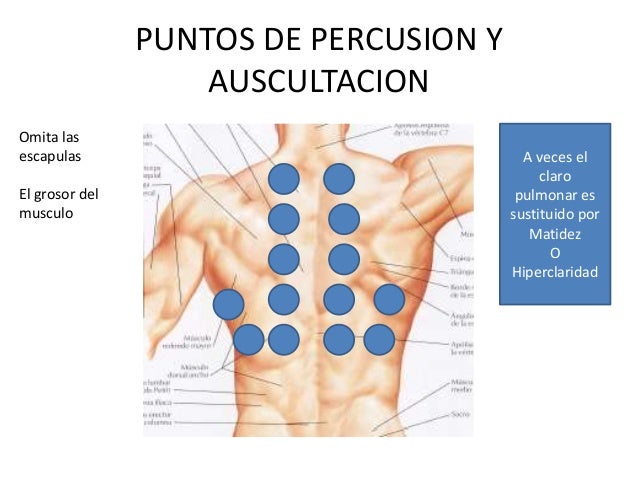
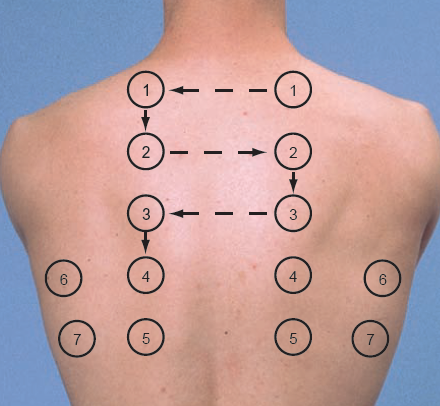
Auscultación
|
|||
Percusión
|
EVALUACION
- - La presión arterial: 160/90 mmHg
- - Frecuencia cardiaca: 110 lpm
- - Tensión pulmonar: 27/15 mmHg
- - Frecuencia respiratoria: 24 rpm
- Edema leve
- Edema leve
- - Temperatura corporal normal
- - Cianosis en labios
- - Ruidos normales, sin soplos cardíacos
- - No refiere dolor
- - El ecocardiograma mostraba signos de sobrecarga
de cavidades derechas
- - La radiografía de tórax fue normal
- En el electrocardiograma se presentan algunos ciclos cardíacos anormales
-Análisis de sangre se presentaron sustancias que hacen que la tensión pulmonar aumente
- En el electrocardiograma se presentan algunos ciclos cardíacos anormales
-Análisis de sangre se presentaron sustancias que hacen que la tensión pulmonar aumente
- - Sistema tegumentario presenta hipo pigmentación
en miembros superiores a nivel de brazo, se observa que su textura es seca pero
se siente uniforme, tipo de piel delgada y pilosa.
- - Sistema neuromuscular presenta alteración ya que
presenta fatiga al momento de realizar transferencias y traslados, también está
afectado el equilibrio.
- - Sistema musculo esquelético afectado porque se
pesó a la paciente, y se relacionó con IMC lo que indica que se encuentra en el
rango de sobrepeso.
- - Dentro de las actividades diarias se encuentra
limitada para realizar actividades de alto esfuerzo e intensidad como carga de
objetos pesados debido a la patología base de su condición que no la permite
desempeñar correctamente sus actividades sin tener repercusiones sobre su
estado de salud, debido a su dificultad para respirar (disnea), sobre todo en
un inicio mientras hace ejercicio y con el tiempo durante el descanso, lo cual
provoca mayor fatiga.
DIAGNOSTICO
Usuario de 29 años con diagnóstico médico
de hipertensión pulmonar, afectando el dominio cardiopulmonar con el patrón A y B. Generando limitaciones en las actividades de la vida diaria y de recreación, en categorías de resistencia/ capacidad aeróbica, ventilación, respiración e intercambio gaseoso; la paciente puede realizar la mayoría de las actividades de la vida diaria como los son: Caminar por tiempo prolongado, trote suave, subir escaleras, vestirse o puede realizar actividades sin sobre exigir sus capacidades y realizándolo con la mayor calma posible para
evitar estrés tanto físico o emocional que puede agravar su condición.
PRONOSTICO
Es buena, debido a que no es muy limitante,
pero es necesario trabajar actividad física regulada para aliviar los síntomas
y evitar mayores complicaciones a futuro.
En pacientes con
hipertensión pulmonar es posible realizar entrenamiento de resistencia (aquel
que busca mejorar la capacidad para mantener una carga durante un tiempo
prolongado) y entrenamiento de fuerza (con el objetivo de mantener y/o mejorar
la masa y la fuerza muscular).
PATOKINESIS
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1b5OeI17_xuFKv0d5nivkBp2TlcU6D-_g
TEST Y MEDIDAS
Se realizaría
pruebas y/o test cardiopulmonares de manera que podamos mantener y mejorar la
capacidad respiratoria del usuario y lograr una mejora en la respiración al tratar
de mejorar el sistema vascular pulmonar para que este pueda lograr una mejor
vasodilatación compensatoria. También se realizarán pruebas, test de sistema osteomuscular
alteración a nivel articular y muscular; en cuanto a su sistema musculoesqueletico
se evaluará si tiene alteraciones posturales, de cambio de posición, equilibrio;
al igual que sistema tegumentario tiene signos para observar si la persona
tiene alguna alteración que pueda influir en el esfuerzo del corazón y pulmones,
debido a la respiración y, algunas pruebas de funcionalidad en la vida diaria.
Dichos test a
realizar son
-
TEST
DE 6 MINUTOS CON DISTANCIA DISMINUIDA: es una prueba que no
requiere demasiado esfuerzo aunque debido a la deficiencia de las capacidades
respiratorias podría no lograr sus expectativas pero se determinaría sus
capacidades cardiopulmonares y proceder a su intervención; por lo tanto la
actividad física no debe ser excesiva sino regulada y supervisada para evitar
mareo, dificultad respiratoria, dolor torácico con el esfuerzo o algunas otras implicaciones.

-
PRESIÓN/
PULSOS CENTRALES Y PERIFÉRICOS: prueba que evalúa el movimiento de la
sangre que recorre órganos y tejidos para determinar posibles insuficiencias
del sistema vascular. dentro de los signos perifericos mas frecuentes que se pueden evidenciar en un paciente con HAP evidenciara generalmente: onda "a" gigante en el pulso venoso yugular y cianosis.
-
SATURACIÓN
DE OXÍGENO Y VOLUMEN DE OXIGENO: Pruebas para determinar el intercambio
gaseoso que existe a nivel pulmonar. Estas pruebas no requieren demasiado sobre
esfuerzo.
https://www.google.com/search?q=saturacion+de&sxsrf=ALeKk02aQ50kHVecvOspOYuiWyqSRu64zQ:1587961459106&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj-g7-14YfpAhWvc98KHXqHDFYQ_AUoAXoECBQQAw&biw=1366&bih=657#imgrc=Gfn2RYgsxAuimM&imgdii=ChO0BBNYxW1pIM
-
PRUEBA
DE FUNCIÓN VENTILATORIA: Se evalúa la actividad de los pulmones en
cuanto a cómo funcionan en las 2 fases
de la respiración que son: inspiración y espiración.


-
AUSCULTACIÓN:
Se realiza para evaluar la integridad de las vías respiratorias.
-
PERCUSIÓN:
Se usa para examinar la presencia de tumores, ya sea para descartar o afirmar
la presencia de estos, también se examinaran los ruidos torácicos para observar
si son normales o anormales.
-
EXPANSIBILIDAD
TORÁCICA: Evaluar el nivel de expansibilidad torácica del usuario para
observar si está en sus valores normales.
-
TIPO
DE TÓRAX: Examinar el tipo de tórax del paciente para evaluar sus
características y adicional a esto observar el patrón respiratorio.

-
TOS:
Evaluar el tipo de tos que presenta el paciente para identificar las
características de esta y poder clasificarla (Seca, Productiva, Aguda o
Crónica).

-
TIPO
DE RESPIRACIÓN: Examinar el tipo de tórax del paciente para evaluar sus
características y adicional a esto observar el patrón respiratorio y el tipo de
respiración (Cheyne-stokes, Biot, Kussmall).

-
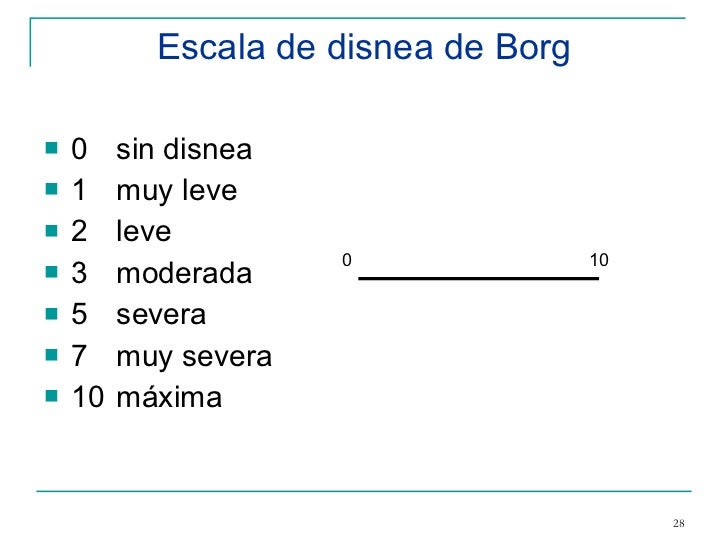
INDICE
DE DISNEA: Se mide con esta escala cuando se detecta que existe alguna
alteración a nivel pulmonar. Se realiza la prueba de respiración y de acuerdo
al resultado indica que tipo de disnea tiene el paciente, en escala de Borg.
-
GASIMETRIA:
Es una prueba con la cual como su nombre lo dice mide los gases de sistema
vascular, así determinar si el patrón respiratorio del paciente se encuentra en
estado óptimo.
- PRUEBA DE ALLEN: Prueba donde se mide que tanto tarda la sangre en llegar a los vasos sanguíneos distales/ periféricos en miembros superiores.

-
SIGNO
DE FÓVEA: Es producido por edema que es el acumulo de liquido en una
parte del cuerpo pero eso especialmente se da en miembros inferiores.
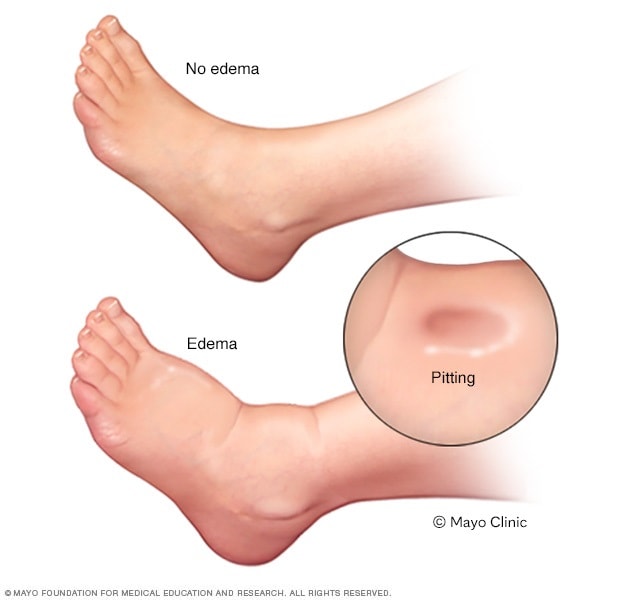
-
ESCALA
DE CLAUDICACIÓN: Se debe realizar la prueba de medición del flujo
sanguíneo cuando el paciente se expone a ejercicio, o actividades de impacto.
https://www.hospitalesperitsant.cat/media/upload/arxius/usuaris/habits_saludables/2012/Malaltia%20aparador%201-%20Dr.%20Cabot.pdf
-
CICLO DE SUEÑO Y VIGILIA: Es realizada cuando la persona no puede conciliar el sueño debido a
dolores, incomodidad o patologías que impiden la quietud.
-
SCREENING
ARTICULAR: Es una prueba usada para evaluar si la persona tiene rangos
de movilidad normal o que no se vean afectados en ningún momento.

-
SCREENIG
MUSCULAR: Es un examen realizado para evaluar la funcionalidad de los músculos
o debilidad de los mismos.

-
INDICE
DE KATZ: Es un tipo de encuesta donde se determina que tanto el
paciente es funcional en cuanto a sus actividades diarias.

-
LAWTON
Y BRODY: Son una serie de preguntas que indican que tanta actividad
tiene el paciente en su vida diaria, entorno de hogar.

-
ESCALA
DE BARTHEL: Se realizan preguntas donde se determina la independencia
que tiene el paciente al realiza actividades de la vida diaria.

-
ESCALA
DE INDEPENDENCIA FUNCIONAL: Es una prueba donde se realizan preguntas
al paciente, de acuerdo a ello se observa que actividades de la vida diaria
están limitadas o si necesita ayuda ¿cuánta?

-
POSTURA (TEST DE PLOMADA): Es la relación de la posición en el
espacio con el cuerpo humano, el examen es realizado para evaluar deficiencias
en la columna vertebral, a nivel torácico o articular de las extremidades.

-
MARCHA: Movimiento del cuerpo en el espacio al
caminar, estos movimientos deben ser simétricos, armónicos, coordinados. Se
puede realizar de forma observable o en un laboratorio especializado con un software
llamado BTS SMART DX.
BALANCE Y EQUILIBRIO (TINETTI): Es la capacidad de reacciones rápidas, automáticas cuando el cuerpo se encuentra en desequilibrio y su centro de gravedad se encuentra desplazado.


https://www.cuerpomente.com/salud-natural/ejercicios/mejores-ejercicios-fortalecer-equilibrio-corporal-mental_4280

BILINGUALISM
CLINICAL CASE PROGRESS
A 29-year-old
woman, who begins in 2014, 4 months after giving birth to her first pregnancy,
begins with exertional dyspnea. These symptoms progressed, for which she was
admitted 13 months after delivery, where the diagnosis of pulmonary
hypertension was made. She was asymptomatic before pregnancy, had no history of
miscarriage, or a personal or family history of pulmonary hypertension and / or
pulmonary thromboembolism. I went through a normal delivery, without
complications, but the delivery turned out to be by means of caesarean section,
although the newborn did not present complications.
CONTEXTUALIZATION
Pulmonary hypertension is a disease of the heart
and lungs since it is high tension in the pulmonary arteries but this causes
the heart, especially the right part, to try harder in pumping blood to the
lungs.
It can be caused by: Rheumatoid arthritis, heart
abnormalities, pulmonary embolism, heart failure, HIV infection, low o2 levels,
COPD, fibrosis, sleep apnea.
Its most common symptoms are: Dyspnea, dizziness,
syncope, pressure or pain in the chest, edema, rapid pulse.
ANAMNESIS
- Age
- Gender
- Life habits
- Drug use
- Family background
- Personal history
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Physical activity
SYSTEMS REVIEW
In the first
instance, an evaluation by systems was performed
CARDIOVASCULAR
|
OSTEOMUSCULAR
|
MUSCULOSKELETAL
|
TEGUMENTARY
|
Blood pressure
|
Muscle screening
|
March
|
Texture
|
Heart rate
|
Joint screening
|
Locomotion
|
Coloration
|
Pulmonary tension
|
Weight
|
Balance
|
Temperature
|
Breathing frequency
|
Size BMI
|
Traslations
|
Elasticity
|
Temperature
|
BMI
|
Consciousness
|
Integrity
|
Edema
|
Posture
|
Behavior
|
Pigmentation
|
Auscultation
|
|||
Percussion
|
EVALUATION
-
The blood pressure was 160/90 mmHg
-
Heart rate 110 bpm
-
Pulmonary pressure 27/15 mmHg
-
Respiratory rate 24 rpm
-
No edema
-
Normal body temperatura
-
Cyanosis on the lips
-
Normal sounds, no heart murmurs
-
The electrocardiogram showed signs of
overloading of the right cavities
-
The chest radiograph was normal.
-
Integumentary system presents hypopigmentation
in upper limbs at arm level, it is observed that its texture is dry but it
feels uniform, thin and hairy skin type.
-
Neuromuscular system presents alteration since
it presents fatigue when making transfers and transfers, balance is also
affected.
-
Musculoskeletal system affected because the
patient was weighed, and was related to BMI, indicating that she is in the
overweight range.
-
Within the daily activities it is limited to
carry out activities of high effort and intensity as a load of heavy objects
due to the base pathology of its condition that does not allow it to carry out
its activities correctly without having repercussions on its state of health,
due to its difficulty. to breathe (dyspnea), especially initially while
exercising and over time during rest, which causes more fatigue.
DIAGNOSIS
The medical diagnosis of the patient affecting the cardiovascular domain with pattern A, but despite its limitations, the patient is functional to carry out most of the activities of daily life without over-demanding his abilities and doing it as calmly as possible to avoid stress. so much physical or emotional that it can aggravate your condition.
PROGNOSIS
It is good,
since it is not very limiting, but it is necessary to work regulated physical
activity to alleviate the symptoms and avoid further complications in the
future.
In patients with
pulmonary hypertension, resistance training (one that seeks to improve the
ability to maintain a load for a long time) and strength training (with the aim
of maintaining and / or improving muscle mass and strength) can be performed.
TEST AND MEASURES
Cardiopulmonary tests and / or tests would be carried out so that we can maintain and improve the user's
respiratory capacity and achieve an improvement in breathing by trying to improve the pulmonary vascular
system so that it can achieve better compensatory vasodilation. Tests, tests of the musculoskeletal system,
alteration at the articular and muscular level will also be carried out; As for his musculoskeletal system, he will
be evaluated for postural changes, changes in position, balance; like integumentary system it has signs to
observe if the person has any alteration that can influence the effort of the heart and lungs, due to breathing.
Some tests of functionality in daily life.
- 6-MINUTE TEST WITH DECREASED DISTANCE:
it is a test that does not require too much effort, although due to the
deficiency of the respiratory capacities it could not meet your expectations
but it would determine your cardiopulmonary capacities and proceed to your
intervention; therefore physical activity should not be excessive but regulated
and supervised to avoid dizziness, respiratory distress, chest pain with
exertion or some other implications.

- CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL PRESSURE /
PULSES: test that evaluates the movement of blood that runs through
organs and tissues to determine possible insufficiencies of the vascular system.

- OXYGEN SATURATION AND OXYGEN VOLUME:
Tests to determine the gas exchange that exists at the lung level. These tests
do not require too much effort.

- VENTILATORY FUNCTION TEST: The
activity of the lungs is evaluated in terms of how they function in the 2
phases of respiration, which are: inspiration and expiration.

- AUSCULTATION: It is performed to
assess the integrity of the airways.

- PERCUSSION: It is used to
examine the presence of tumors, either to rule out or confirm the presence of
these, chest sounds will also be examined to see if they are normal or
abnormal.

- THORACIC EXPANSIBILITY: Evaluate
the user's level of thoracic expandability to see if it is at its normal
values.

- THORAX TYPE: Examine the
patient's chest type to evaluate its characteristics and, in addition to this,
observe the respiratory pattern.

- CYANOSIS: Examine the patient
for cyanosis and if it is present, if it disappears with O2 or not.

- COUGH: Evaluate the type of
cough that the patient presents to identify its characteristics and to classify
it (Dry, Productive, Acute or Chronic).

- TYPE OF BREATH: Examine the
patient's chest type to evaluate its characteristics and, in addition to this,
observe the respiratory pattern and the type of breathing (Cheyne-stokes, Biot,
Kussmall).

- DISNEA INDEX: This scale is
measured when an alteration is detected at the lung level. The breathing test
is performed and according to the result indicates what type of dyspnea the
patient has, on a Borg scale.

- GASIMETRY: It is a test with
which, as its name says, it measures the gases of the vascular system, thus
determining if the patient's respiratory pattern is in an optimal state.

- ALLEN TEST: Test where it is
measured how long it takes for the blood to reach the distal / peripheral blood
vessels in the upper limbs.

- SIGN OF FOVEA: It is
produced by edema that is the accumulation of liquid in a part of the body but
that especially occurs in the lower limbs.

- CLAUDICATION SCALE: The blood flow measurement test must be
performed when the patient is exposed to exercise or impact activities.

- SLEEP AND WATCH CYCLE: It is performed when the person cannot fall asleep due to pain, discomfort
or pathologies that prevent quiet.

https://www.google.com/search?q=ciclo+de+sue%C3%B1o+y+vigilia&sxsrf=ALeKk027IloJKcT4_jpBSIosvSoq7f
3l6w:1590395156481&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjzwurSy87pAhUshOAKHb97DvgQ_AUoA
XoECA0QAw&biw=1366&bih=657#imgrc=MvBIHPburSAgIM&imgdii=hPT0iIZ5APz3-M
- ARTICULAR SCREENING: It is a test used to assess whether the person has ranges of normal mobility or
that they are not affected at any time.

https://www.semiologiaclinica.com/index.php/articlecontainer/examenfisico/106-examen-fisico-neurologico-normal
- MUSCULAR SCREENIG: It is an examination made to evaluate the functionality of the muscles or their weakness.

- KATZ INDEX: It is a type of
survey where it is determined how much the patient is functional in terms of
their daily activities.

- LAWTON AND BRODY: They are a
series of questions that indicate how much activity the patient has in his
daily life, home environment.

- BARTHEL SCALE: Questions are
asked where the independence of the patient when carrying out activities of
daily life is determined.

- FUNCTIONAL INDEPENDENCE SCALE:
It is a test where questions are asked to the patient, according to which it is
observed that activities of daily life are limited or if you need help, how
much?

- POSTURE (PLUMB TEST): It is the relationship of the position in space with the human body, the examination
is performed to evaluate deficiencies in the spine, at the thoracic or articular level of the extremities.

- MARCH: Movement of the body in space when walking, these movements must be symmetrical, harmonic,
coordinated. It can be done in an observable way or in a specialized laboratory with software called
BTS SMART DX.

- BALANCE AND BALANCE (TINETTI): It is the capacity of fast, automatic reactions when the body is in
imbalance and its center of gravity is displaced.




REFERENCIAS
-
Medline. (2020). Hipertensión pulmonar. Recuperado
el 22 de Mayo de 2020 de, https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/000112.htm
-
Mayoclinic. (2017). Hipertensión pulmonar.
Recuperado el 22 de Mayo de 2020 de, https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-hypertension/symptoms-causes/syc-20350697